Exploring the Galaxies: A Journey Through the Cosmos
The universe is a vast and mysterious expanse, filled with billions of galaxies, each containing countless stars, planets, and other celestial phenomena. Exploring these galaxies not only enhances our understanding of the cosmos but also deepens our appreciation for the intricate tapestry of existence. In this blog, we will embark on a journey through the galaxies, examining their formation, structure, and the exciting discoveries that await us.
What Are Galaxies?
Galaxies are massive systems composed of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, and dark matter, all bound together by gravity. They come in various shapes and sizes, with the three main types being:
Spiral Galaxies: Characterized by their spiral arms winding outward from the center, these galaxies often contain young stars and abundant gas and dust. The Milky Way, our home galaxy, is a classic example of a spiral galaxy.
Elliptical Galaxies: These galaxies have a more rounded, oval shape and typically contain older stars with less gas and dust. They are often found in clusters and can range from small to giant in size.
Irregular Galaxies: Lacking a distinct shape, irregular galaxies are often chaotic in appearance and can be rich in star formation. They are usually smaller and can be the result of gravitational interactions with other galaxies.
The Formation of Galaxies
The formation of galaxies is a complex process that began shortly after the Big Bang, approximately 13.8 billion years ago. Initially, the universe was a hot, dense soup of particles. As it expanded and cooled, matter began to clump together under the influence of gravity, forming the first stars and galaxies.
Over billions of years, galaxies evolved through processes such as mergers and interactions. When two galaxies collide, they can trigger bursts of star formation and lead to the creation of new structures. Understanding these processes helps astronomers piece together the history of the universe and the evolution of galaxies.
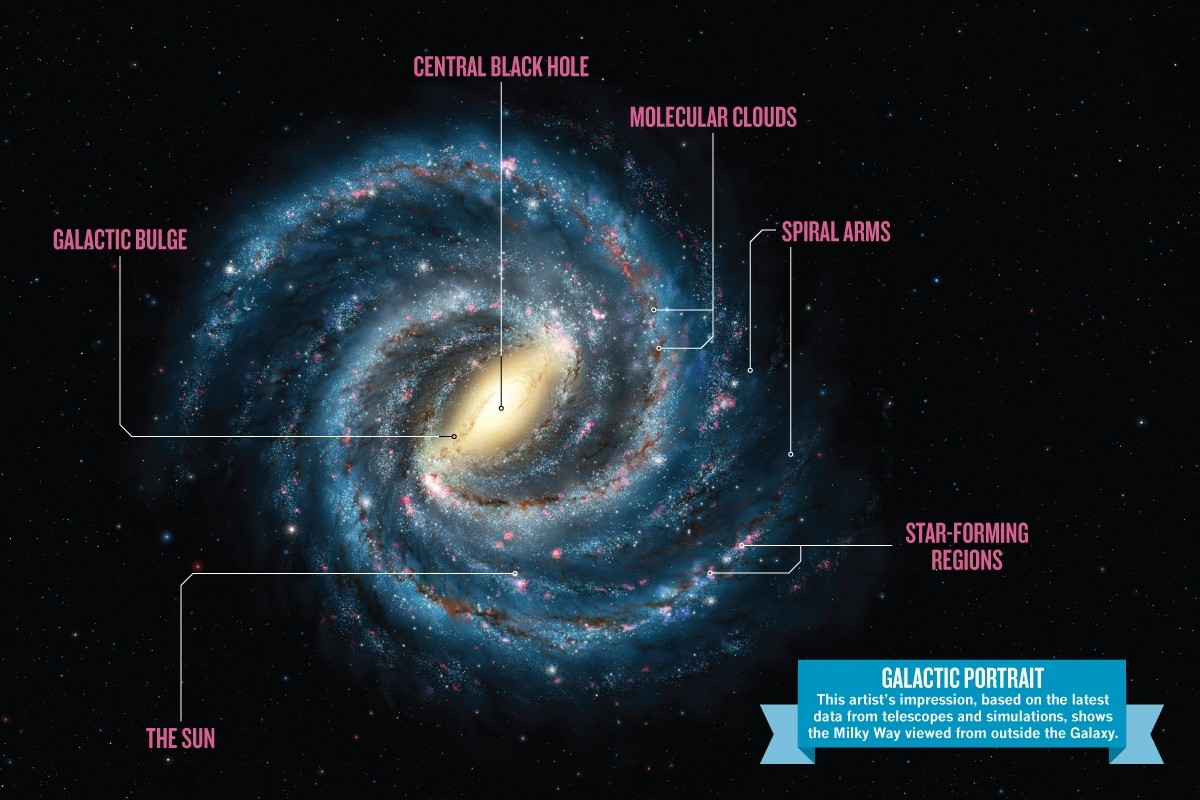
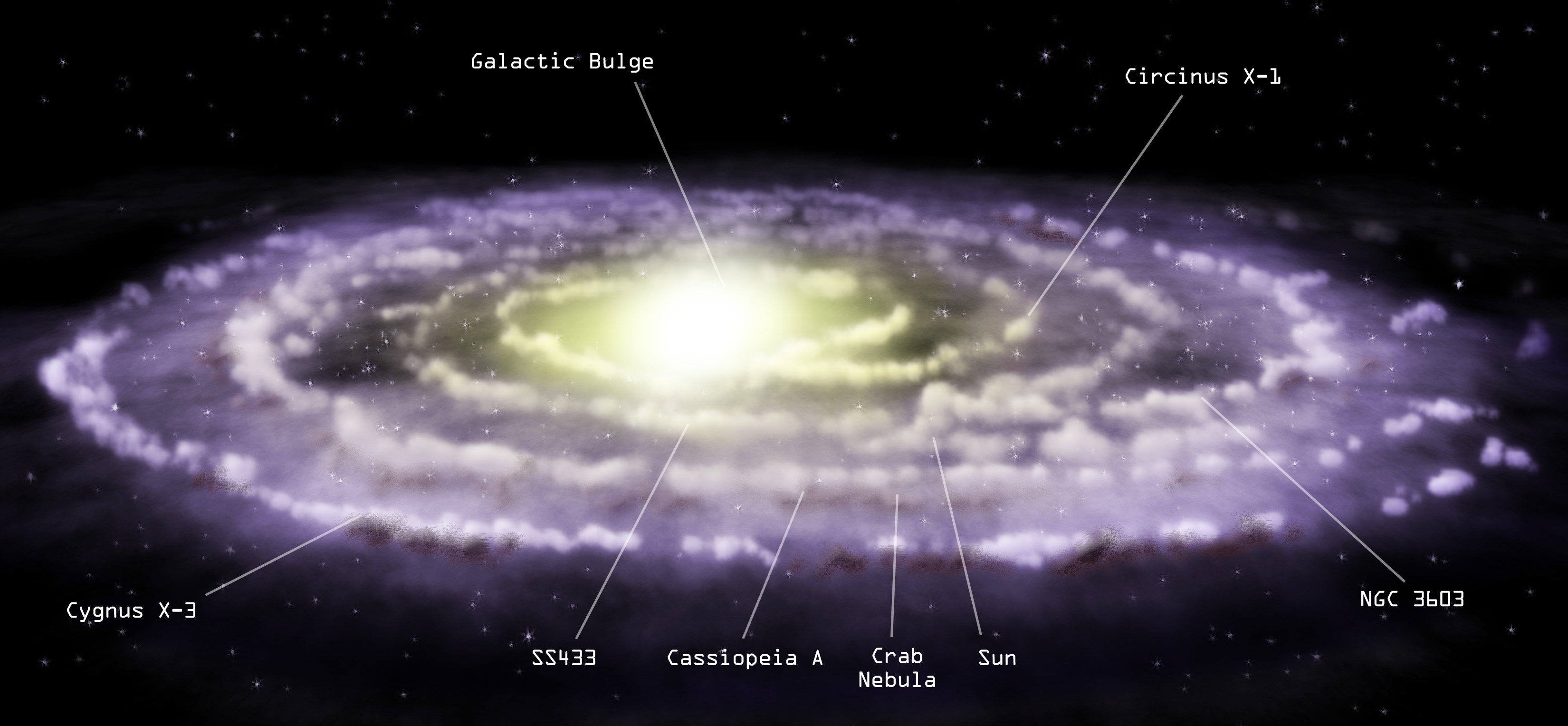
The Milky Way: Our Galactic Home
The Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy that contains an estimated 100 to 400 billion stars, along with a vast array of planets, moons, and other celestial objects. It spans about 100,000 light-years in diameter and is home to our solar system, located about 27,000 light-years from the galactic center.
The study of the Milky Way provides valuable insights into the nature of galaxies as a whole. Observations of its structure, star formation rates, and the distribution of dark matter help astronomers understand the dynamics of galaxies and their evolution over time.
Exploring Other Galaxies
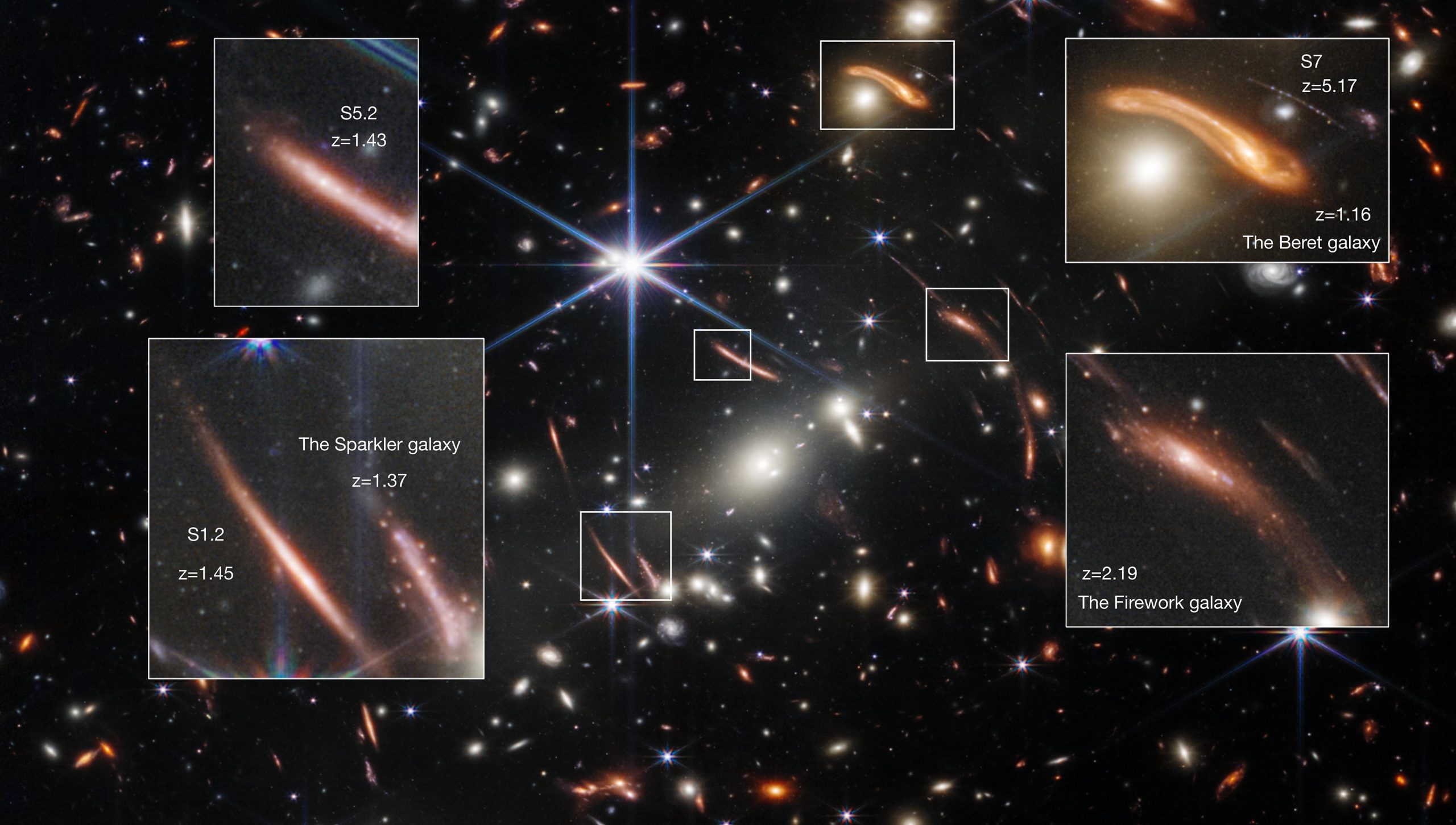
While the Milky Way is our immediate focus, astronomers have made significant strides in exploring other galaxies. The advent of powerful telescopes and advanced imaging techniques has allowed us to observe galaxies billions of light-years away, providing a glimpse into the early universe.
Notable Galaxies to Explore:
Andromeda Galaxy (M31): The closest spiral galaxy to the Milky Way, Andromeda is on a collision course with our galaxy. In about 4.5 billion years, the two galaxies are expected to merge, creating a new galactic structure.
Whirlpool Galaxy (M51): This stunning spiral galaxy is known for its well-defined spiral arms and is interacting with a smaller galaxy, NGC 5195. The gravitational interaction has created beautiful tidal features and enhanced star formation.
Sombrero Galaxy (M104): Named for its sombrero-like shape, this spiral galaxy is notable for its bright nucleus and prominent dust lane. It is a popular target for amateur astronomers and professional studies alike.
Messier 87 (M87): This giant elliptical galaxy is famous for being the first galaxy to have its supermassive black hole imaged by the Event Horizon Telescope in 2019. The image provided groundbreaking evidence of black holes' existence and their role in galaxy formation.
The Role of Dark Matter and Dark Energy
One of the most intriguing aspects of galaxy exploration is the role of dark matter and dark energy. Dark matter, which makes up about 27% of the universe, is an invisible substance that does not emit light or energy. Its presence is inferred from its gravitational effects on visible matter, such as stars and galaxies.
Dark energy, on the other hand, is believed to be responsible for the accelerated expansion of the universe, making up about 68% of the cosmos. Understanding these mysterious components is crucial for comprehending the overall structure and fate of galaxies and the universe itself.
The Future of Galactic Exploration
As technology continues to advance, the future of galactic exploration looks promising. Upcoming missions and telescopes, such as the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), are set to revolutionize our understanding of galaxies. JWST will allow astronomers to observe distant galaxies in unprecedented detail, shedding light.






Comments
Post a Comment